Nettraf: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
Zur Navigation springen
Zur Suche springen
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
||
| Zeile 4: | Zeile 4: | ||
[[Bild:nettraff-client.jpg]][[Bild:nettraf-stat.jpg]] | [[Bild:nettraff-client.jpg]][[Bild:nettraf-stat.jpg]] | ||
'''Vorgehen:''' | |||
Die Datei sollte für das Zielsystem kompiliert werden. Ich habe das in einer EFW Build-Umgebung kompiliert, früher habe ich das auch schon für den IPCop so gemacht. | |||
* Sourcen laden, auspacken und in das Verzeichnis wechseln | |||
* Kompilieren mit ''make'' | |||
* Die Datei ''src/nettraffd'' nach ''/usr/sbin'' kopieren | |||
* Ein Startscript erstellen (Aufruf: ''/usr/sbin/nettraffd -D'') | |||
That's it. | |||
Mein Startscript für die Endian Firewall in ''/etc/init.d/nettraf'': | |||
<pre> | |||
#!/bin/sh | |||
# | |||
# chkconfig: 345 81 19 | |||
# description: nettraffd is the network traffic logging daemon | |||
# | |||
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions | |||
function start() | |||
{ | |||
printf "Starting %s: " "nettrafd" | |||
/usr/sbin/nettrafd -D | |||
echo | |||
touch /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd | |||
} | |||
function stop() | |||
{ | |||
printf "Stopping %s: " "nettrafd" | |||
killproc nettrafd | |||
echo | |||
rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd | |||
} | |||
function reload() | |||
{ | |||
pid=`pidof nettrafd` | |||
if [ "x$pid" != "x" ]; then | |||
kill -HUP $pid 2>/dev/null | |||
fi | |||
touch /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd | |||
} | |||
case "$1" in | |||
start) | |||
start | |||
;; | |||
stop) | |||
stop | |||
;; | |||
restart) | |||
stop | |||
start | |||
;; | |||
reload) | |||
reload | |||
;; | |||
status) | |||
status nettrafd | |||
;; | |||
*) | |||
printf "Usage: %s {start|stop|status|restart|reload}\n" "nettrafd" | |||
exit 1 | |||
esac | |||
exit 0 | |||
</pre> | |||
Version vom 15. Januar 2007, 00:01 Uhr
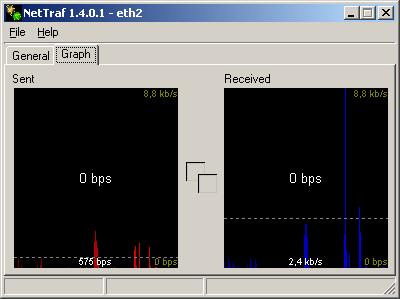
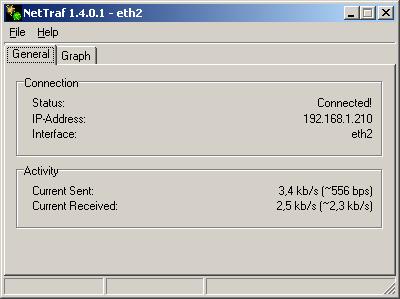
Netzwerk Monitor für EFW (Nettrafd)
Ich habe ein kleines Tool gesucht, das mir den aktuellen Traffic zum Internet anzeigt. Nettraf hat sich auf dem IPCop über fast 2 Jahre als stabil und nützlich gezeigt. Das Tool ist trivial zu installieren, ganz nach dem Motto KISS ("keep it short and simple").
Vorgehen:
Die Datei sollte für das Zielsystem kompiliert werden. Ich habe das in einer EFW Build-Umgebung kompiliert, früher habe ich das auch schon für den IPCop so gemacht.
- Sourcen laden, auspacken und in das Verzeichnis wechseln
- Kompilieren mit make
- Die Datei src/nettraffd nach /usr/sbin kopieren
- Ein Startscript erstellen (Aufruf: /usr/sbin/nettraffd -D)
That's it.
Mein Startscript für die Endian Firewall in /etc/init.d/nettraf:
#!/bin/sh
#
# chkconfig: 345 81 19
# description: nettraffd is the network traffic logging daemon
#
. /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions
function start()
{
printf "Starting %s: " "nettrafd"
/usr/sbin/nettrafd -D
echo
touch /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd
}
function stop()
{
printf "Stopping %s: " "nettrafd"
killproc nettrafd
echo
rm -f /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd
}
function reload()
{
pid=`pidof nettrafd`
if [ "x$pid" != "x" ]; then
kill -HUP $pid 2>/dev/null
fi
touch /var/lock/subsys/nettrafd
}
case "$1" in
start)
start
;;
stop)
stop
;;
restart)
stop
start
;;
reload)
reload
;;
status)
status nettrafd
;;
*)
printf "Usage: %s {start|stop|status|restart|reload}\n" "nettrafd"
exit 1
esac
exit 0